Diabetes mellitus is a chronic endocrine pathology that develops in people with insulin resistance and pancreatic dysfunction. accompanied by persistent hyperglycemia. Patients are constantly thirsty, complain of frequent emptying of the bladder. The disease is based on a deficiency of its own insulin against the background of an increased glucose level. Against the background of diabetes, appetite is often disturbed, general well-being worsens, wounds and ulcers do not heal well. The disease is chronic, characterized by a constant progression. The lack of therapy is fraught with strokes, kidney failure, heart attack, and a significant decrease in visual acuity. A sudden fluctuation in blood sugar can cause a hyperglycemic or hypoglycemic coma.
Symptoms

Diabetes mellitus develops gradually, in the early stages there may be no specific symptoms. Often a violation is discovered by chance, during the next scheduled inspection.
Disease progression leads to complaints of:
- thirst and dry mouth
- insomnia
- cramps in the lower extremities
- itchy skin
- disability
- decreased emotional lability
- profuse and frequent urination
- increased appetite
- dryness of the skin and mucous membranes, which is fraught with cracks, ulcerative lesions
- Decreased visual acuity.
Regeneration processes slow down: wounds, ulcers, cuts heal for a long time. Decreases sensitivity in the legs, up to total numbness. The progression of obesity is possible. As the disease spreads, the hair on the legs begins to fall out, while the hairiness of the skin on the face may increase. Xanthomas form on the body - small yellow formations.
The genitourinary system often suffers: vulvovaginitis is often diagnosed in women, and balanoposthitis in women. Metabolic processes are disturbed, defenses are lowered, the body becomes less resistant to infectious injuries. Prolonged lack of medical care can lead to osteoporosis. This is accompanied by complaints of pain in the joints and spine, deformation of the bones and violations of their integrity.
Causes
Diabetes mellitus is accompanied by tissue resistance to insulin. This means that they become less sensitive to the effects of insulin. At the same time, the insulin level in the blood plasma often remains within the normal range, and the sugar level rises significantly. The disease is often diagnosed in patients of older age groups.
Among the predisposing factors that cause a violation, are:
- hereditary predisposition
- nutritional errors
- cardiovascular diseases
- chronic stress
- adrenal cortex insufficiency
- overweight
Diabetes can develop against the background of prolonged use of certain groups of drugs.
insulin resistance
Insulin resistance is a pathological condition that underlies the mechanisms of development of diabetes mellitus. In the body, the sensitivity of tissues to the action of insulin decreases. There may be no specific symptoms. Violation is accompanied by excess body weight, increased blood pressure.
In patients, the progression of fatty hepatosis of the liver is observed, hyperpigmented areas may form on the skin - black acanthosis. To identify a violation, it is necessary to take a blood test for glucose, insulin, check the HOMA index. The basis of therapy is the correction of the diet, moderate physical activity.
Over weight

Overweight people are at risk: adipose tissue blocks tissue susceptibility to the effects of insulin. This is one of the key factors that leads to the development of the disease. Excess weight is detected in more than 89% with diabetes. The cause of such a violation may be maintaining a sedentary lifestyle, hereditary predisposition, metabolic disorders. Medical correction, the study of the psychological state, the selection of a suitable diet are required.
pancreatic tumor
Pancreatic tumors can cause diabetes in people of different age groups. These growths are usually benign and do not cause specific symptoms until they become large. The lack of timely therapy is fraught with the transformation of a benign tumor into a malignant one. At the same time, symptoms of general intoxication appear, compression of surrounding organs is observed, vessels and nerve endings suffer.
To confirm the diagnosis, the following diagnostic studies are involved:
- Tumor markers
- computed tomography
- magnetic resonance imaging
- puncture
- biopsy
The treatment protocol is selected individually. In most cases, surgery is indicated. With the malignancy of the pathological process, a course of chemotherapy and radiation therapy is additionally prescribed.
sedentary lifestyle
With a lack of motor activity, the mitochondria - the power stations of every cell in the body - suffer. This entails a disruption in the functioning of internal organs, a deterioration in mood and a tendency to depression. Many diabetes patients tend to take advantage of stress, they rarely play sports. Even 15-minute daily workouts can activate metabolic processes, improve cell susceptibility to insulin, and reduce the risk of diabetes. If it is not possible to practice daily, a walk in the fresh air at a fast pace is shown. It is recommended to walk and spend in the fresh air for at least half an hour a day.
Cardiovascular diseases
Under the influence of cardiovascular diseases, the sensitivity of tissues to insulin decreases and the risk of developing diabetes mellitus increases.
People who have been diagnosed with such disorders should show the utmost vigilance:
- atherosclerosis
- arterial hypertension
- coronary artery disease.
Ischemic heart disease is a myocardial injury that occurs when the blood supply to the heart muscles is insufficient. It is the most frequent cause of death, exceeding 75%. It is most often observed in patients with hypertension, hyperlipidemia, hypodynamia, obesity, as well as in smokers. It is important to treat the root causes of the disease in a timely manner, regularly examined by a cardiologist.
inadequate nutrition

A significant factor is the diet of people with diabetes. They are prone to overeating, while suffering from a nutrient deficiency. They often have a deficiency of such essential substances:
- minerals including chromium, selenium, manganese, iron, zinc, copper
- polyunsaturated fatty acids: healthy fats found in wild fish, lard, quality cold-pressed vegetable oils
- protein, which is the building material for new cells and tissues
- fat-soluble substances: vitamins A, E, D.
The diet is often dominated by simple carbohydrates and sugar, which negatively affect the intestinal microflora and reduce the protective properties of the body. If an excessive amount of sugar and carbohydrates enter the body, this causes glucose surges and overloads the pancreas.
endocrine diseases
Diabetes mellitus can develop against the background of endocrine diseases:
- pancreatitis
- pituitary insufficiency
- hypothyroidism
- hyperthyroidism
- thyrotoxicosis
- dysfunction of the adrenal glands.
In this case, it requires a complex effect on the root cause that caused the diabetes. Patients are often prescribed hormonal drugs - courses or on a regular basis. It is also important to eliminate the source of stress, normalize sleep. It is important to ensure sufficient intake of iodine, selenium, zinc and iron to ensure normal function of the endocrine glands.
Infectious diseases
The manifestation of diabetes mellitus is often observed with a long-term progressive infectious disease:
- herpes
- viral hepatitis
- herpes
Chronic infection depletes the body's defenses, making it more susceptible to other diseases. The primary manifestation of hepatitis can become a symptom of a viral disease. In this case, it is important to work with the root cause - the source of infection and reduce the viral load in the body. To do this, use antiviral drugs, immunostimulants, drugs for symptomatic correction.
medicines
Certain groups of drugs can also provoke the manifestation of diabetes in older or middle-aged people.
The risk group includes people who take:
- synthetic corticosteroids
- diuretic drugs
- cytostatics
Medicines can only be taken as prescribed by a doctor. If drugs cause insulin resistance with an increased risk of developing diabetes, it is advisable to reconsider the appointment, adjust the dosage and choose alternative means to replace it. It is impossible to prescribe or stop taking drugs on your own, since this can worsen the course of the underlying disease, for the treatment of which the described drugs were recommended.
Chronic insufficiency of the adrenal cortex
Adrenal insufficiency often leads to the development of diabetes. It occurs in patients with insufficient hormonal secretion from the adrenal glands. Characteristic symptoms: bronze pigmentation of the skin, mucous membranes, a feeling of weakness, vomiting, diarrhea, impaired consciousness. Accompanied by fluid and electrolyte disturbances, dysfunction of the cardiovascular system. Treatment is carried out in a complex way: the root cause is eliminated, corticosteroids, symptomatic drugs are used.
Possible complications

The lack of timely treatment of diabetes mellitus is fraught with such complications:
- Diabetic angiopathy: increased vascular permeability, increased risk of thrombosis, cardiovascular diseases.
- Diabetic foot: occurs in the context of circulatory disorders in the lower extremities.
- Trophic ulcers in the lower extremities.
- Diabetic polyneuropathy, a condition that affects the peripheral nerves, occurs in more than 70% of patients with diabetes. Over time, polyneuropathy can transform into neuropathy. This complication is rare, but requires timely and high-quality medical care.
- Diabetic nephropathy, in which it affects the blood supply to the vessels of the kidneys and increases the likelihood of developing kidney failure.
- Diabetic coma is the most dangerous complication that is fraught with death.
Hyperglycemia occurs when there is a significant increase in blood glucose. This is accompanied by weakness, malaise, loss of appetite, headache. If proper measures are not taken, the patient begins to feel sick, the vomit has the smell of acetone. Relieves pain in the abdomen, lowers blood pressure. To prevent dangerous complications, it is important to start treatment for insulin resistance/diabetes mellitus in a timely manner and constantly monitor blood glucose levels. It is impossible to select drugs on your own, since they may not have the proper therapeutic result and lead to complications.
Which doctor to contact
At the first symptoms of diabetes, it is recommended to consult an endocrinologist. The doctor will make a comprehensive diagnosis using laboratory and instrumental techniques, determine the degree of progression of the disorder. In the future, consultations with other doctors may be required: a cardiologist, a nutritionist, an oncologist, a gynecologist. It is important to follow all the doctors' instructions and refrain from self-medication.
Diagnostics
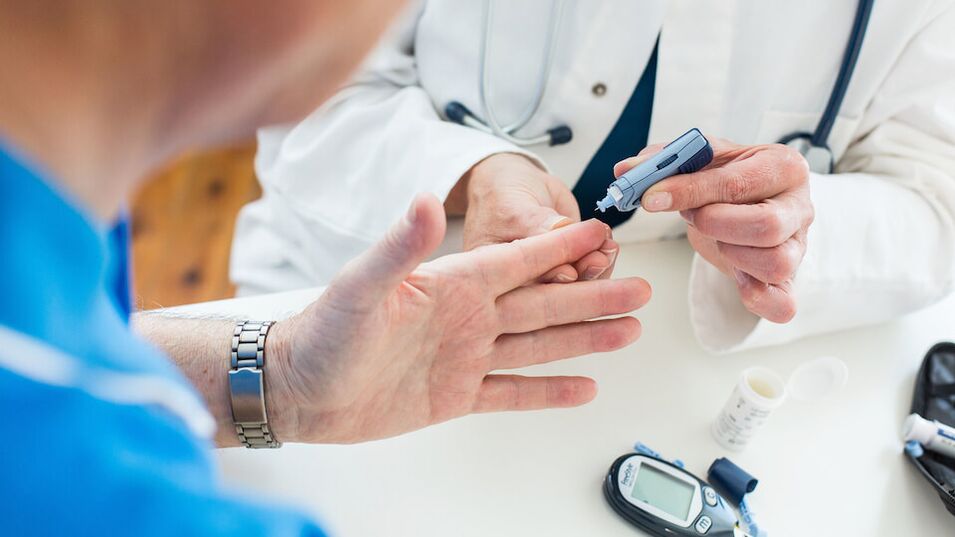
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes a full diagnosis:
- blood glucose on an empty stomach
- ketone bodies and sugar in the urine
- glycosylated hemoglobin
- C-peptide
- insulin
- glucose tolerance test.
To determine sugar in urine, special test strips are used. For the timely detection of complications of diabetes mellitus, it is recommended to carry out an ultrasound examination of the kidneys, reovasography of the extremities, and also to check the structural and functional state of the brain.
Treatment
The treatment protocol is selected for each patient individually. At the same time, age, concomitant chronic somatic diseases are taken into account. Therapy is carried out for life, the patient must be under the constant supervision of an endocrinologist. At the first stage, they review the diet, reduce the number of meals.
The optimum is two meals a day, without snacks. Breakfast with healthy fats, proteins and carbohydrates can be obtained from vegetables. Bakery products, sources of sugar and other simple carbohydrates are completely eliminated from the diet. The portions are small, they provide satiety due to the balanced composition and the presence of fat.
Drug correction involves the use of such groups of drugs:
- hypoglycemic agents
- drugs to restore blood circulation and microcirculation
- high blood pressure medications (if indicated)
The treatment regimen is selected individually and is often supplemented with vitamin-mineral complexes, amino acids - taurine, glycine. Medications will not help eliminate the problem completely. The patient is required to have a responsible attitude towards lifestyle correction and compliance with all the doctor's recommendations.
Patients with diabetes are shown moderate physical activity. This prevents further progression of the pathological process and the development of complications. Recommended daily walk, yoga, swimming, gymnastics, breathing exercises. The best option: classes under the supervision of an instructor. It is recommended to discuss the volume of loads with the doctor in advance.
Prevention

To prevent diabetes, it is important to control the diet, normalize body weight, eliminate the source of stress, restore the mode of work, rest and sleep. It is important to review the diet, include a sufficient amount of healthy fats, fiber and reduce simple carbohydrates. It is important to restore sleep: go to bed no later than 23: 00, sleep in a cool dark room.
Particular attention is paid to physical activity: daily walk in the fresh air, running, brisk walking, swimming and any other type of physical activity suitable and feasible. Physical inactivity is unacceptable and can aggravate the course of insulin resistance. Breathing practices are helpful: pranayama, Buteyko breathing, to ensure sufficient oxygen supply to the tissues.
People and risk groups are recommended to monitor the indicators of glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin, insulin. At the first sign of a violation, refuse self-treatment and turn to an experienced endocrinologist.
The prognosis for patients who immediately sought medical help and reviewed their lifestyle is mostly favorable. They can live long, quality lives without facing the dangerous complications of the disease. The lack of therapy leads to a reduction in life expectancy and acute/chronic complications.